Intro.
A query string in the context of a web API is a part of a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) that is used to pass parameters or data to a web server when making a GET request. It's a way to specify additional information or criteria for the server to use when processing the request.
The query string is typically located after the question mark (`?`) in a URL and consists of one or more key-value pairs separated by ampersands (`&`).
Here's a basic structure of a URL with a query string:
```
https://example.com/api/endpoint?param1=value1¶m2=value2¶m3=value3
```
In the above URL:
- `https://example.com/api/endpoint` is the base URL or endpoint of the API.
- `?` indicates the start of the query string.
- `param1`, `param2`, and `param3` are parameter names.
- `value1`, `value2`, and `value3` are the corresponding values for those parameters.
APIs use query strings for various purposes, including:
1. **Filtering Data**: You can use query parameters to filter or narrow down the data you want from the API. For example, in a product catalog API, you could use a query string to specify the category or price range of products you want to retrieve.
2. **Pagination**: Query parameters are often used for pagination, allowing you to request a specific page of results or a specific number of items per page.
3. **Sorting**: You can specify how the results should be sorted, such as ascending or descending order, using query parameters.
4. **Search**: In search APIs, you can pass search queries in the query string to retrieve results that match your search criteria.
5. **Authentication**: Some APIs require authentication tokens or API keys, which can be passed as query parameters for authorization.
For example, in a fictional API for searching books, you might use a query string like this to search for books with a specific title:
```
https://api.example.com/books/search?title=programming
```
The server processes the query string parameters and provides a response based on the criteria specified in the query.
Reading API documentation is a crucial skill for a software engineer, Here's a step-by-step guide on how to navigate API documentation to find the endpoints you're looking for using Reddit Data API as an example
Authentication and Authorization: Reddit uses OAuth2 for authentication. You can find details on how to authenticate in the Reddit OAuth2 documentation. It explains the steps to obtain an access token.
First check for access roles, like : API access rules which states that :
Endpoint List: In Reddit's API documentation, you can find the list of endpoints in the API Endpoints section.
Example :
"GET [/r/subreddit]/api/user_flair":An HTTP GET request to retrieve a list of available user flair for the current subreddit. User flair is a way for Reddit users to display custom text or icons next to their username in a specific subreddit. However, it's important to note that this API endpoint has certain conditions under which it may not return flair data. These conditions include when flair is disabled on the subreddit, when users cannot set their own flair, or when they are not moderators with the privilege to set flair.
Here's how you can use Python to make this GET request using the `requests` library:

The subreddit name is the name of the specific community on RedditFor example, if you want to retrieve user flair for the "programming" subreddit, you would replace "YOUR_SUBREDDIT_NAME"with"programming"like this:In this example:
- Replace `"YOUR_SUBREDDIT_NAME"` with the name of the subreddit for which you want to retrieve user flair.
- Set the `User-Agent` header to identify your application. Reddit requires a User-Agent header with a meaningful value; it should not be empty.
Here's an example of a User-Agent string for a web browser:
Mozilla/5.0- The GET request is made to the specified URL, and the response is checked for its status code.
- If the status code is 200 (OK), the response data is assumed to be in JSON format, and it's printed to the console. This data will contain information about the available user flair for the specified subreddit.
Ensure you have the `requests` library installed in your Python environment. You can install it using `pip install requests`.
Also in documentation, look for the following :
Parameters: This endpoint takes
{subreddit}as a parameter, which should be replaced with the name of the subreddit you want information about. The parameter is a part of the URL.Response Information: The response for this endpoint is in JSON format, and the structure of the response is detailed in the documentation. It includes information about the subreddit.
Rate Limiting and Quotas: Reddit imposes rate limits on their API. You can find details in the API Rules section. Make sure to respect these limits to avoid being rate-limited.
Code Examples: Reddit's API documentation includes code examples in different programming languages to help you understand how to make requests.
Pagination:
Using an API with pagination involves retrieving a large set of data in smaller, manageable chunks or pages. This is a common practice when dealing with APIs that return a large number of records, such as lists of items, search results, or social media posts. Pagination allows you to reduce the amount of data transferred in a single request and improves performance.
Here's how to use an API with pagination:
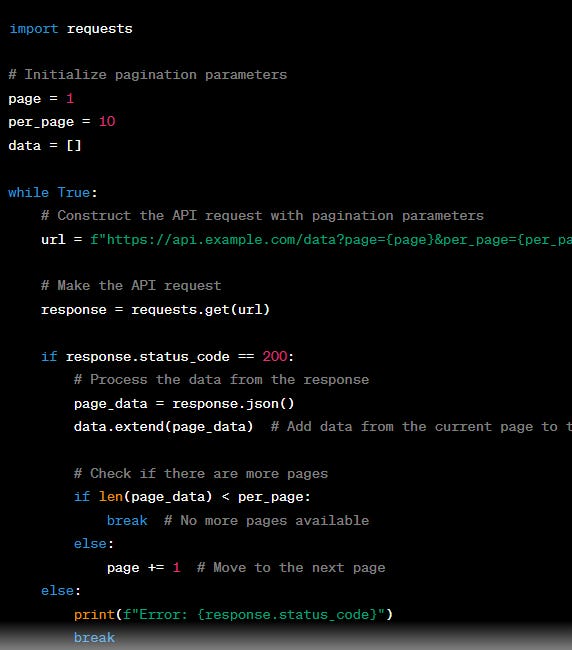
page variable to prepare for the next request, ensuring you retrieve all the paginated data.How to parse JSON results from an API:
Parsing JSON results from an API is a common task in software development, especially when interacting with web services that return data in JSON format. Here are the steps to parse JSON results from an API using Python:
1. **Make an API Request:**
- First, use a library like `requests` to make a GET request to the API's endpoint.
```python
import requests
response = requests.get("https://api.example.com/data")
```
2. **Check the Response Status:**
- Ensure the response status code is 200, indicating a successful request.
```python
if response.status_code == 200:
```
3. **Parse JSON Data:**
- Use the `
json()` method provided by the `requests` library to parse the JSON response into a Python data structure, typically a dictionary or a list.
```python
data = response.json()
```
4. **Access JSON Data:**
- Now, you can access the data in the parsed JSON as you would with any Python data structure. For example, if the JSON response contains a dictionary with a key named "items," you can access it like this:
```python
items = data["items"]
```
- If the data contains nested structures, you can navigate through the JSON to access specific values.
5. **Iterate Through JSON Arrays:**
- If the JSON response contains an array of items, you can iterate through it using a `for` loop to process each item individually.
```python
for item in items:
# Process each item here
```
6. **Handle Error Conditions:**
- Implement error handling to deal with potential issues, such as invalid JSON or network errors.
```python
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
```
Here's a complete example:
```python
import requests
# Make the API request
response = requests.get("https://api.example.com/data")
# Check the response status code
if response.status_code == 200:
# Parse the JSON data
data = response.json()
# Access specific data
items = data["items"]
# Iterate through the items
for item in items:
print(item["name"]) # Assuming "name" is a key in the JSON data
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
```
In this example, we've made an API request, checked the status code, parsed the JSON response, and processed the data. You can adapt this code to work with different APIs and JSON data structures based on the API's documentation and the specific data you need.
LIMIT:
Let's consider a simple example using the JSONPlaceholder API to retrieve and limit the response to the first 5 posts. JSONPlaceholder is a fake online REST API for testing and prototyping.
Here's a Python script that uses the `requests` library to make a GET request and limit the response to the first 5 posts:
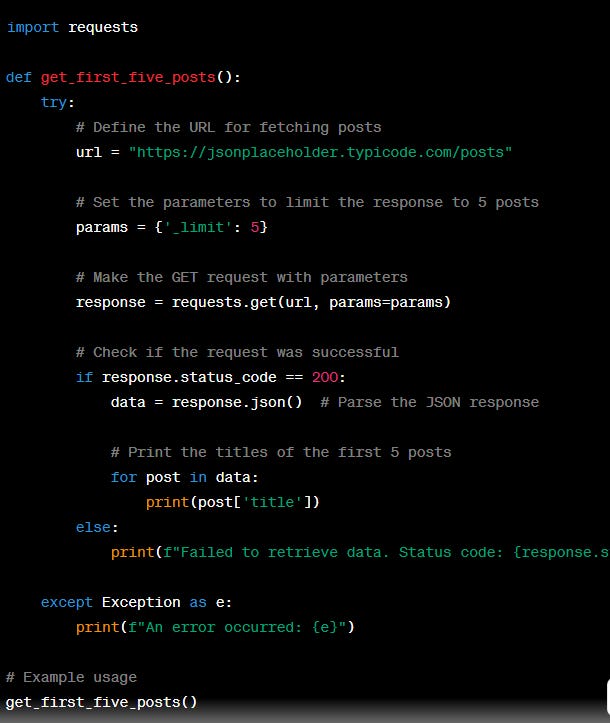
_limit in the params dictionary, which limits the response to the first 5 postsIn this example, we specify the parameter `_limit` in the `params` dictionary, which limits the response to the first 5 posts. You can adjust this value to limit the response to any desired number of posts.
Notes : To sort a dictionary by its values in Python, you can use the sorted() function along with a lambda function as the sorting key. Here's how you can do it:
In this example, we first have a dictionary called my_dict with key-value pairs. To sort it by values, we use the sorted() function, passing in the items() method of the dictionary as the iterable to be sorted. The key parameter is set to a lambda function that extracts the values (item[1]) from each key-value pair. This sorts the dictionary in ascending order of values.
How to use recursion to paginate an API response ?
Using recursion to paginate through an API response is a common technique in software engineering, especially when dealing with APIs that return a large number of results. Here's a general outline of how you can use recursion to paginate through an API response:
Define a Function: Start by defining a function that will make the API request and handle pagination. This function should accept parameters for the API endpoint, any required query parameters, and the current page number.
Make the API Request: Inside the function, make an API request to the specified endpoint, including the page number as a query parameter. This will retrieve a page of results.
Process the Response: After receiving the API response, you need to process the data in the response, perform any necessary operations, and handle the results. You may want to extract the relevant data from the response.
Check for Pagination: Examine the response to determine if there are more pages of results available. This can usually be determined by looking at the response metadata, such as the presence of a "next page" link or a "total pages" field.
Recursion: If there are more pages to retrieve, call the same function recursively, incrementing the page number for the next request. Pass in the updated page number and any other necessary parameters.
Termination Condition: Define a termination condition for the recursion. This condition should be met when there are no more pages to fetch. For example, you can check if the "next page" link is null or if the current page number exceeds the total number of pages.
Combine and Return Data: As you make each API request and receive responses, combine the data from all pages into a single dataset, which can be returned as the final result once the recursion is complete.
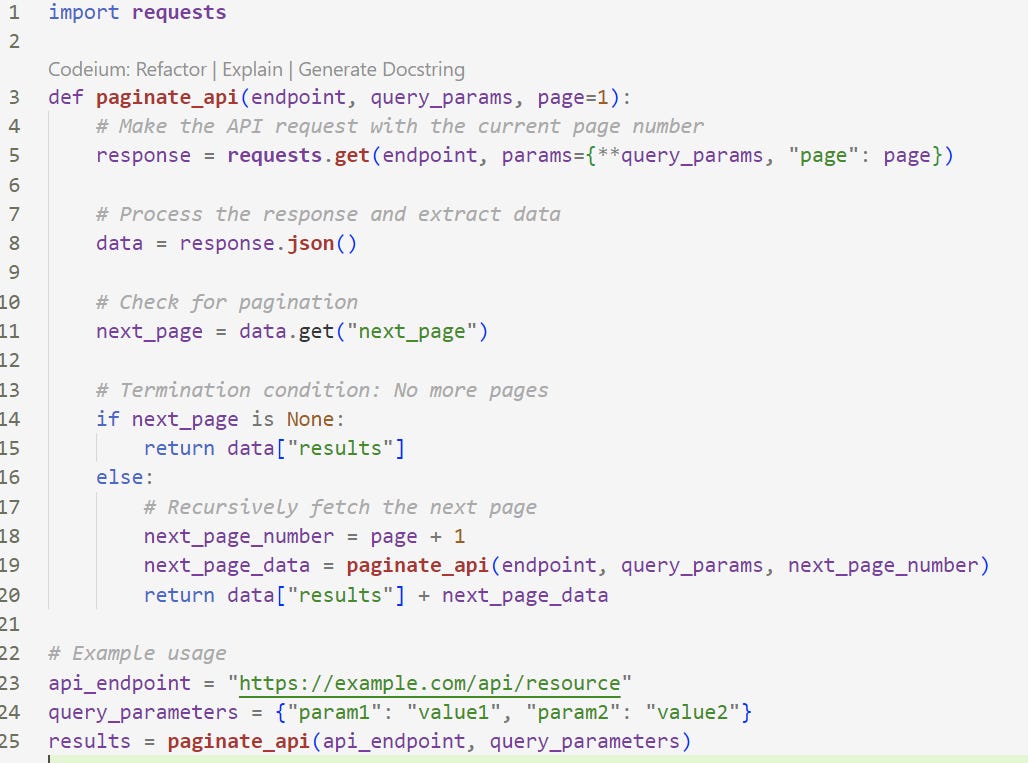
data["results"] represents the data from the current page. It's assumed that the API response contains a field called "results" that holds the actual data you are interested in. - `next_page_data` represents the data obtained from the next page. During each recursive call to the `paginate_api` function, you fetch data from the next page.Note 1:
return data["results"] + next_page_data
This line of code is combining the results obtained from the current page with the results obtained from the next page during the recursive API pagination. Let me break it down for you:
The `+` operator is used to concatenate (combine) the data from the current page (`data["results"]`) with the data from the next page (`next_page_data`). This way, you're creating a cumulative list of results that includes data from all pages you've fetched.
By using this approach, you ensure that the data from all pages is collected and returned as a single list. This is often done when dealing with paginated API responses to aggregate all the relevant information into a single dataset for further processing or analysis.
Note 2:
Reddit Documentation :
To page through a listing, start by fetching the first page without specifying values for after and count. The response will contain an after value which you can pass in the next request. It is a good idea, but not required, to send an updated value for count which should be the number of items already fetched.
Resources:






