Databases and SQL - 1
0x0D. SQL - Introduction - SQL - MySQL - install MySQL 8.0 on an Ubuntu 20.04 _ SQL on VSC - DDL - DML
Intro.
What's a Relational Database: A relational database is a type of database that organizes and stores data in structured tables with rows and columns. It's based on the principles of the relational model, which emphasizes the relationships between different pieces of data. In a relational database, you have multiple tables, and you can establish connections between them using keys. This structure makes it easy to query and manipulate data using a standardized language called SQL.
SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Not Only SQL) are two different types of database management systems, each with its own strengths and use cases. Here's a brief overview of the differences between the two and when to use each:
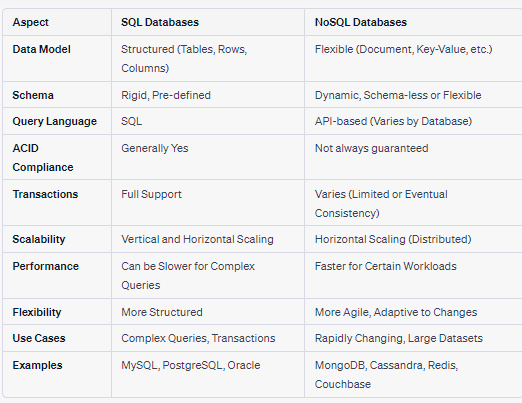
A schema, in the context of databases, refers to the logical structure or blueprint that defines how data is organized, stored, and accessed within a database management system. It specifies the tables, columns, relationships, constraints, and other elements that define the structure of the data.
Install MySQL version 8.0 on an Ubuntu 20.04 server:
Check the version of Ubuntu using a command-line prompt.
sudo apt install lsb-releaselsb_release -a
sudo apt updatesudo apt upgradesudo apt install mysql-serverBy this we installed
MySQL, let’s configure it:sudo mysql
To solve Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Followhttps://www.databasestar.com/access-denied-for-user-root-at-localhost/
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'your_new_password';The mysql_native_password method is a traditional method of authentication and will allow you to login.
Step 5: Flush the privileges, which tells the server to refresh the grant tables and apply your changes, with this command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
What’s MySQL ?
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is widely used for storing, managing, and retrieving structured data. It is one of the most popular and well-known database systems in the world. MySQL is designed to efficiently handle various types of data, from small personal projects to large-scale enterprise applications.
How to create a database in MySQL ?
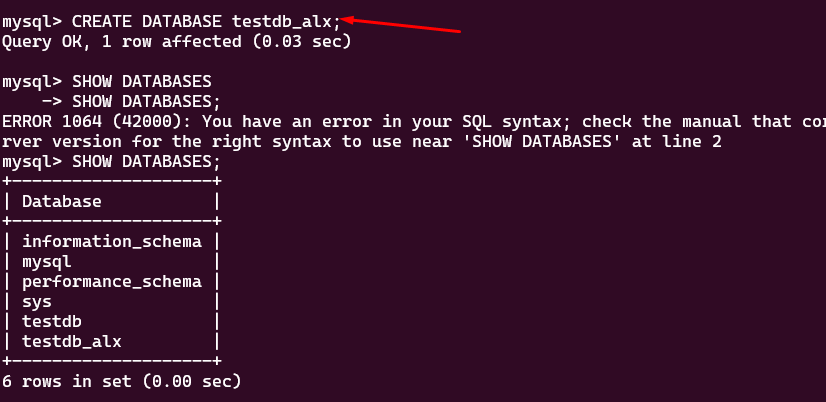
To create a database in MySQL, you can use the SQL `CREATE DATABASE` statement. Here's how you can do it:
1. **Open MySQL Command-Line Client**:
Open your terminal or command prompt and start the MySQL command-line client by entering the following command. You will be prompted to enter your MySQL root password.
mysql -u root -p
2. **Create a Database**:
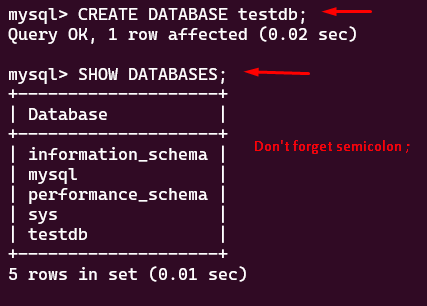
Once you are in the MySQL command-line client, you can use the `CREATE DATABASE` statement to create a new database. Replace `your_database_name` with the desired name for your database.
CREATE DATABASE mydb;
3. **Verify Database Creation**:
You can verify that the database was created by listing all the databases:
SHOW DATABASES;
This will display a list of all the databases, including the one you just created.
4. **Exit MySQL Command-Line Client**:
To exit the MySQL command-line client, simply enter:
exit;
What does DDL and DML stand for ?
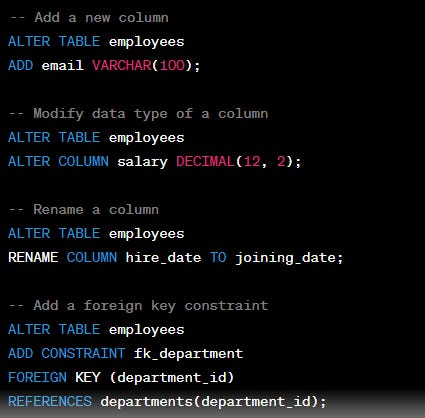
DDL (Data Definition Language): DDL stands for Data Definition Language. It consists of SQL statements that are used to define and manage the structure of a database, including tables, indexes, constraints, and other database objects. DDL statements do not directly interact with the data within the database; rather, they define how the data is organized and stored. Common DDL statements include CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and TRUNCATE.
Examples of DDL statements:
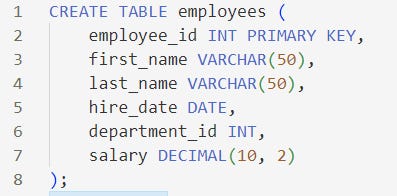
CREATE TABLE: Defines a new table and its columns.ALTER TABLE: Modifies an existing table's structure.DROP TABLE: Deletes a table from the database.DROP TABLE employees;CREATE INDEX: Creates an index on one or more columns for efficient data retrieval.CREATE INDEX idx_last_name ON employees (last_name);
2. DML (Data Manipulation Language): DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. It consists of SQL statements that are used to manipulate and interact with the data stored within a database. DML statements are responsible for adding, retrieving, updating, and deleting data records in the database. Common DML statements include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Examples of DML statements:
SELECT: Retrieves data from one or more tables based on specified conditions.INSERT INTO: Adds new records into a table.-- Insert a new employee recordINSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, hire_date, department_id, salary)VALUES ('John', 'Doe', '2023-08-15', 3, 55000.00);-- Insert multiple records in a single queryINSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, hire_date, department_id, salary)VALUES('Alice', 'Smith', '2023-07-01', 1, 60000.00),('Bob', 'Johnson', '2023-07-15', 2, 52000.00);UPDATE: Modifies existing records in a table.
-- Update an employee's salary
UPDATE employees
SET salary = 60000.00
WHERE employee_id = 101;
DELETE FROM: Removes records from a table based on specified conditions.
-- Delete an employee record
DELETE
FROM employees
WHERE employee_id = 102;
Write SQL on VSC:
To connect Visual Studio Code to MySQL and execute SQL queries, you would typically use an extension like "SQLTools" or "MySQL" to achieve this functionality. Here's how you can set it up using the "SQLTools" extension:
1. **Install SQLTools Extension**:
- Open Visual Studio Code.
- Go to the Extensions view by clicking on the square icon in the sidebar on the left or pressing `Ctrl+Shift+X`.
- Search for "SQLTools" in the Extensions view search bar.
- Install the "SQLTools" extension by Matheus Teixeira.
2. **Connect to MySQL Server**:
- After installing the extension, you should see a "SQLTools" icon (database icon) in the sidebar on the left.
- Click on the "SQLTools" icon to open the SQLTools panel.
- In the SQLTools panel, click on the "Add New Connection" button.
- Select the database system (MySQL) and enter your connection details (host, port, username, password, etc.).
- Test the connection to ensure it's working.
3. **Execute SQL Query**:
- Open your SQL file (`test.sql`) in Visual Studio Code.
- Highlight the `CREATE TABLE` query or any other query you want to execute.
- Right-click on the highlighted query.
- From the context menu, select "Run SQL Query."
Have a question ? Drop it here …
JOIN:
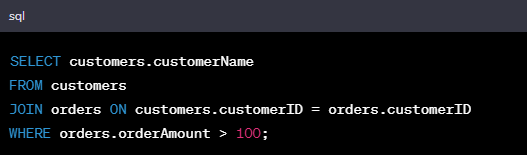
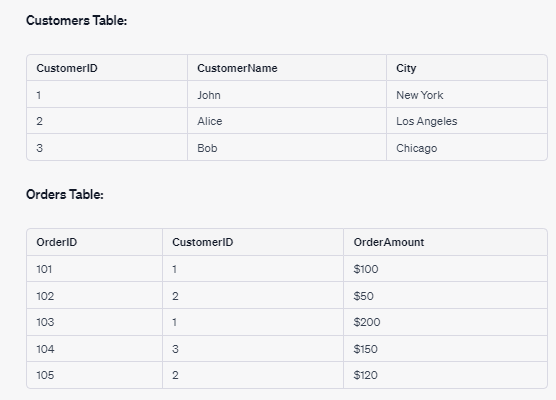
In the context of relational databases, a "join" is an operation that combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. Joins are used to retrieve data from multiple tables by matching rows that have a common value in the specified columns. This allows you to combine data from different tables to create more meaningful and comprehensive results.
Let’s write a query to retrieve customer names from the "customers" table for customers who have placed orders with an amount greater than 100 in the "orders" table.
Notes on practice:
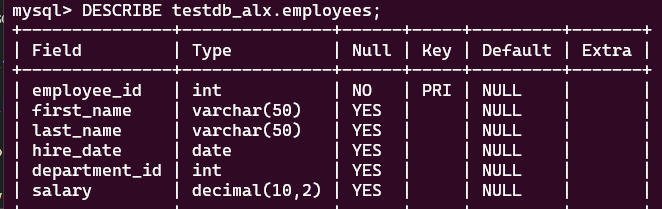
2 ways to show a table description :
mysql> SHOW COLUMNS FROM testdb_alx.employees;mysql> DESCRIBE testdb_alx.employees;
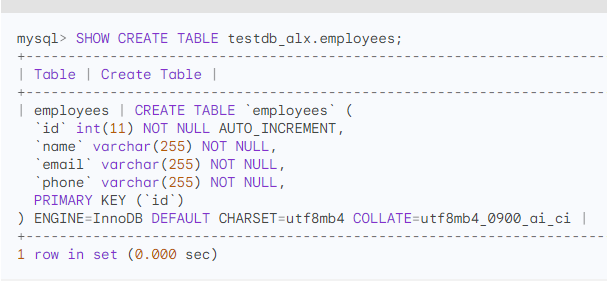
If need to retrieve the SQL statement that was used to create a specific table. It provides you with the exact SQL syntax that was used to define the table, including column definitions, data types, constraints, and indexes.
Here's the syntax of the
SHOW CREATE TABLEstatement:SHOW CREATE TABLE table_name;
FUNCTIONS:
The COUNT()
function in MySQL is used to count the number of rows in a table or the number of rows that match a specified condition. The COUNT() function has three forms:
COUNT(*): This form counts all the rows in the table, including NULL values.COUNT(column_name): This form counts the number of rows in the specified column, excluding NULL values.COUNT(DISTINCT column_name): This form counts the number of distinct rows in the specified column, excluding NULL values.
For example, the following query will count the number of rows in the employees table:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees;This query will return the number of rows in the employees table, including NULL values.
The following query will count the number of rows in the employees table where the name column is not NULL:
SELECT COUNT(name) FROM employees;This query will return the number of rows in the employees table where the name column is not NULL.
The following query will count the number of distinct employees in the employees table:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT name) FROM employees;This query will return the number of distinct employees in the employees table.
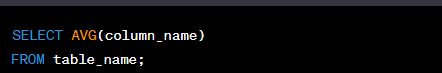
AVG()
a Function to calculate the average (mean) value of a column in a table. Here's the basic syntax:
Example:
SELECT AVG(revenue)
FROM sales;
GROUP BY clause:
The GROUP BY clause in MySQL is used to group rows that have the same values into summary rows. This can be used to perform calculations on the grouped data, such as finding the average, minimum, maximum, or count of the values in a column.
The GROUP BY clause is typically used with aggregate functions, such as COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MAX(), and MIN().
For example, the following query will group the rows in the customers table by the country column and return the number of customers in each country:
SELECT country, COUNT(*) AS num_customers
FROM customers
GROUP BY country;This query will return one row for each unique country in the customers table. The country column will contain the name of the country, and the num_customers column will contain the number of customers in that country.
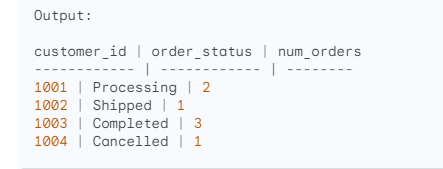
The GROUP BY clause can also be used to group rows by multiple columns. For example, the following query will group the rows in the orders table by the customer_id and order_status columns:
SQL
SELECT customer_id, order_status, COUNT(*) AS num_orders
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id, order_status;
This query will return one row for each unique combination of customer_id and order_status in the orders table. The customer_id column will contain the customer ID, the order_status column will contain the order status, and the num_orders column will contain the number of orders for that customer with that order status.
The GROUP BY clause is a powerful tool that can be used to analyze data in MySQL. By grouping rows and using aggregate functions, you can quickly and easily get insights into your data.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about the GROUP BY clause in MySQL:
The GROUP BY clause must be used with a SELECT statement.
The GROUP BY clause must be placed after the WHERE clause.
The columns or expressions in the GROUP BY clause must be either numeric or non-null character columns.
You can use the HAVING clause after the GROUP BY clause to filter the results of the query.
Resources :
MySQL Tutorial for Beginners [Full Course]
The big NoSQL databases comparison
SQL COMMANDS C H E AT S H E E T
Next Part 2 : …..








Amazing posts, greaaat <3