Advanced MySQL -- TLDR
Back-end - SQL - MySQL - functions - triggers - indexing - procedures - views
A refresher :
log into a MySQL database server from the command line. Here's a breakdown of the command:
mysql -u root -p
Databases: Create a new database.
CREATE DATABASE new_db;To Show Tables in a Specific Database: If you want to list tables from a specific database without selecting it first, use:
SHOW TABLES IN database_name;Tables: Create a new table within a database.
CREATE TABLE employees (id INT, name VARCHAR(50));Insert Rows: Insert a new row into a table.
INSERT INTO employees (id, name) VALUES (1, 'John Doe');Select: Retrieve data from a table.
SELECT * FROM employees;Scenarios:
Imagine we have a sales table that records sales transactions. The table has the following columns: transaction_id, product_id, quantity, and sale_date.
Objective:
We want to find the total quantity sold for each product and order the results by the total quantity in descending order.
SELECT product_id, SUM(quantity) AS total_quantity
FROM sales
GROUP BY product_id
ORDER BY total_quantity DESC;2. Subtracting Two Columns
Suppose you have a table named orders with columns total_amount and discount. To find the net amount for each order after subtracting the discount, you would use the following query:
SELECT total_amount, discount, (total_amount - discount) AS net_amount
FROM orders;3.IFNULL is a function in MySQL that allows you to return an alternate value if an expression is NULL. It is particularly useful in scenarios where you need to ensure that a NULL value does not cause issues in your data processing or display.
SELECT salary, bonus, salary + IFNULL(bonus, 0) AS total_compensation
FROM employees;Update & Delete: Update existing data and delete a row.
UPDATE employees SET name='Jane Doe' WHERE id=1;
DELETE FROM employees WHERE id=2;Alter table:
Suppose you have a table named employees and you want to change the column name from empName to employeeName:
ALTER TABLE employees CHANGE COLUMN empName employeeName VARCHAR(100);
Autocommit, Commit, Rollback: Control transactions.
START TRANSACTION;
UPDATE employees SET salary=5000 WHERE id=1;
COMMIT; -- Save changes
ROLLBACK; -- Undo changesNote: The AUTOCOMMIT mode is typically enabled by default in MySQL. This means that every single SQL statement is treated as a transaction and is automatically committed right after it is executed. If you want to disable this automatic commit mode, you can use the SET autocommit=0; command.
Date and Time :
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS TEST(
my_date DATE,
my_time TIME,
my_datetime DATETIME
);
INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(CURRENT_DATE(), CURRENT_TIME(), Now())
Stored procedures
Why: Stored procedures are fast because they reduce network traffic and benefit from MySQL's caching mechanism, similar to prepared statements.
Example: Imagine you have a web application that needs to perform a complex data processing task involving multiple SQL queries. If you execute these queries individually from your application, each query incurs network overhead. With a stored procedure, you send just one request to the database, the procedure runs all the queries on the server, and only the final result is sent back, reducing the network load
Creating a Stored Procedure:
example, but for adding books to a bookstore database. We'll assume you have two tables: authors and books. The procedure will add a new book, and if the author of the book doesn't exist in the authors table, it will add the author as well.
Database Tables:
authors: Contains information about authors (author_id,name).books: Contains information about books (book_id,title,author_id).
Stored Procedure: AddBook
This procedure will take the name of an author and the title of a book. It will add the author to the authors table if they don't already exist, and then add the book to the books table, linking it to the author.
Assumptions:
The
authorstable has columnsauthor_id(auto-increment, primary key) andname.The
bookstable has columnsbook_id(auto-increment, primary key),title, andauthor_id.
SQL Script:
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE AddBook(
IN book_title VARCHAR(255),
IN author_name VARCHAR(255)
)
BEGIN
-- Variable to hold author_id
DECLARE author_id INT;
-- Check if the author exists and get the author_id
SELECT author_id INTO author_id FROM authors WHERE name = author_name;
-- If the author does not exist, insert the author and get the new author_id
IF author_id IS NULL THEN
INSERT INTO authors (name) VALUES (author_name);
SET author_id = LAST_INSERT_ID();
END IF;
-- Insert the book with the obtained author_id
INSERT INTO books (title, author_id) VALUES (book_title, author_id);
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Explanation:
Author Check: The procedure first checks if the author already exists in the
authorstable. If not, it inserts the new author.Inserting the Book: The book is then added to the
bookstable with the correctauthor_id, linking it to its author.LAST_INSERT_ID(): This function is used to get the ID of the last inserted row, which is useful when the author is newly added.
Triggers in MySQL
Triggers in MySQL are a powerful feature that allow you to automatically execute a specified set of SQL statements when certain database events occur. Here are key aspects of using triggers in MySQL
Trigger Events: Triggers can be associated with three types of database events:
INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETE.Trigger Time: Triggers can be set to activate either
BEFOREorAFTERthe associated event.NEW and OLD Keywords: Within trigger bodies, you can use
NEWto refer to the state of a row after anINSERTorUPDATEoperation, andOLDto refer to the state of a row before anUPDATEorDELETEoperation.Creating Triggers: Use the
CREATE TRIGGERstatement to create a trigger. The syntax is as follows:
Examples:
After Delete Trigger: Performs actions after a row is deleted. For example, to update a count in another table after a row is deleted:
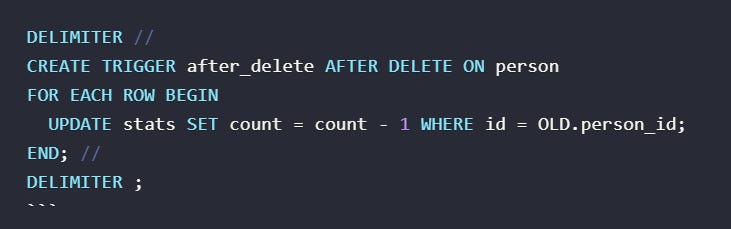
SHOW TRIGGERS; command, which displays all triggers in the current database, including their names, associated tables, and trigger events.CREATE FUNCTION
The
CREATE FUNCTIONstatement is used to create a stored function, which is similar to a stored procedure but must return a single value.
Example: Create a function named GetTotal that calculates the total amount by multiplying quantity and price.
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION GetTotal(quantity INT, price DECIMAL(10,2)) RETURNS DECIMAL(10,2)
BEGIN
DECLARE total DECIMAL(10,2);
SET total = quantity * price;
RETURN total;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Differences Between Procedures and Functions
Return Value: Functions must return a value using
RETURN, while procedures do not return a value but can return parameter values usingOUTorINOUTparameters.Invocation: Functions can be called from within SQL statements (like
SELECT), whereas procedures are invoked using theCALLstatement.Invoke function :
Invoke the Procedure:
Purpose: Procedures are generally used for executing business logic and operations on the database, while functions are typically used for computations and can return results.
View
A MySQL view is a virtual table created from an SQL query, featuring rows and columns similar to a regular table. It simplifies complex queries, enhances security by restricting access to underlying tables, and allows data to be presented in a more useful structure. Views also create a consistent layer, masking changes in table structures and minimizing the impact on applications using the database.
Example :
Indexing
How Indexes Improve Performance:
Speeding Up Searches: Indexes can significantly speed up data retrieval operations, especially in large tables.
Optimized Join Operations: In tables with foreign key relationships, indexes can make join operations more efficient.
Trade-offs:
Increased Storage: Indexes require additional disk space.
Slower Write Operations: Inserting, updating, or deleting rows in an indexed table can be slower because the index also needs to be updated.
How to import a SQL dump
example
cat employyes .sql | mysql -uroot -p myDB
Enumeration and Default Values
We create an
enumcolumn, you specify a list of possible values this column can hold. If you don't explicitly set a value for this column when inserting a row, the database automatically assigns the first value in the defined enumeration list as the default value.
Example :
Suppose we have a table called Orders where there's a column named Status. This Status column is intended to represent the current state of an order, such as Pending, Shipped, Delivered, etc.
Here's how you might define this using an enum:
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT,
Status ENUM('Pending', 'Shipped', 'Delivered', 'Cancelled') DEFAULT 'Pending',
);Resources
MySQL Full Course for free 🐬 (2023)
VSC extension :
Revise MYSQL Essentials ON :








